- Research Article
- Open access
- Published:
The Existence and Uniqueness of Solution of Duffing Equations with Non-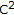 Perturbation Functional at Nonresonance
Perturbation Functional at Nonresonance
Boundary Value Problems volume 2008, Article number: 859461 (2008)
Abstract
This paper deals with a boundary value problem for Duffing equation. The existence of unique solution for the problem is studied by using the minimax theorem due to Huang Wenhua. The existence and uniqueness result was presented under a generalized nonresonance condition.
1. Introduction
In recent years, many authors are greatly attached to investigation for the existence and uniqueness of solution of Duffing equations, for example, [1–11], and so forth. Some authors ([8, 11, 12], etc.) proved the existence and uniqueness of solution of Duffing equations under  perturbation functions and other conditions at nonresonance by employing minimax theorems. In 1986, Tersian investigated the equation
perturbation functions and other conditions at nonresonance by employing minimax theorems. In 1986, Tersian investigated the equation  using a minimax theorem proved by himself and reaped a result of generalized solution [13]. In 2005, Huang and Shen generalized the minimax theorem of Tersian in [13]. Using the generalized minimax theorem, Huang and Shen proved a theorem of existence and uniqueness of solution for the equation
using a minimax theorem proved by himself and reaped a result of generalized solution [13]. In 2005, Huang and Shen generalized the minimax theorem of Tersian in [13]. Using the generalized minimax theorem, Huang and Shen proved a theorem of existence and uniqueness of solution for the equation  [14] under the weaker conditions than those in [13].
[14] under the weaker conditions than those in [13].
Stimulated by the works in [13, 14], in the present paper, we investigate the solutions of the boundary value problems of Duffing equations with non- perturbation functions at nonresonance using the minimax theorem proved by Huang in [15].
perturbation functions at nonresonance using the minimax theorem proved by Huang in [15].
2. Preliminaries
Let  be a real Hilbert space with inner product
be a real Hilbert space with inner product  and norm
and norm  , respectively,
, respectively,  and
and  be two orthogonal closed subspaces of
be two orthogonal closed subspaces of  such that
such that  . Let
. Let  denote the projections from
denote the projections from  to
to  and from
and from  to
to  , respectively. The following theorem will be employed to prove our main theorem.
, respectively. The following theorem will be employed to prove our main theorem.
Theorem 2.1 (see [15]).
Let  be a real Hilbert space, let
be a real Hilbert space, let  and
and  be orthogonal closed vector subspace of
be orthogonal closed vector subspace of  such that
such that  , let
, let  be an everywhere defined functional with Gâteaux derivative,
be an everywhere defined functional with Gâteaux derivative,  everywhere defined and hemicontinuous. Suppose that there exist two continuous functions
everywhere defined and hemicontinuous. Suppose that there exist two continuous functions  satisfying
satisfying

for  ,
,  ,
,  ,
,  ,
,  ,
,  . Then, the following hold:
. Then, the following hold:
(a) has a unique critical point
has a unique critical point  such that
such that  ;
;
(b) .
.
It is easy to prove the following corollary of the above theorem.
Corollary 2.2.
Let  be a real Hilbert space, let
be a real Hilbert space, let  and
and  be orthogonal closed vector subspace of
be orthogonal closed vector subspace of  such that
such that  , and let
, and let  be an everywhere defined functional with second Gâteaux differential. Suppose that there exist two continuous functions
be an everywhere defined functional with second Gâteaux differential. Suppose that there exist two continuous functions  satisfying
satisfying

for  ,
,  ,
,  ,
,  ,
,  ,
,  ,
,  . Then, the following hold:
. Then, the following hold:
(a) has a unique critical point
has a unique critical point  such that
such that  ;
;
(b) .
.
Proof.
We note that  is a second Gâteaux differentiable functional, the mean-value theorem ensures that there exists
is a second Gâteaux differentiable functional, the mean-value theorem ensures that there exists  such that
such that  . Therefore, for
. Therefore, for  ,
,  ,
,  ,
,  ,
,  ,
,  , we have
, we have

The conclusion of the corollary follows immediately from Theorem 2.1.
3. The Main Theorems
Consider the boundary value problem

where  ,
,  is a potential Carathéodory function,
is a potential Carathéodory function,  is a given function in
is a given function in  .
.
Let  , then (3.1) may be written in the form of
, then (3.1) may be written in the form of

where  . Clearly,
. Clearly,  is a potential Carathéodory function, and if
is a potential Carathéodory function, and if  is a solution of (3.2), then
is a solution of (3.2), then  will be a solution of (3.1).
will be a solution of (3.1).
It is well known that  is a Hilbert space with inner product:
is a Hilbert space with inner product:

and norm  , respectively. The system of trigonometrical functions,
, respectively. The system of trigonometrical functions,

is a system of orthonormal functions in  . Each
. Each  can be written as the Fourier series
can be written as the Fourier series

Define the linear operator  ,
,

Denote

Clearly,  is a self-adjoint operator, and
is a self-adjoint operator, and  is a Hilbert space for the inner product:
is a Hilbert space for the inner product:

 , the norm induced by this inner product is
, the norm induced by this inner product is

Note that  is not a space.
is not a space.
Since  in (3.1), and hence
in (3.1), and hence  in (3.2), is a potential Carathéodory function, there exists a function
in (3.2), is a potential Carathéodory function, there exists a function  such that
such that

and hence

and the mapping  , and hence
, and hence  , generates a Nemytskii operator
, generates a Nemytskii operator  by
by

and hence

Define the functional  by
by

where  satisfies (3.10) and
satisfies (3.10) and  is in (3.1). We have
is in (3.1). We have

It is easy to see that

where  . Clearly,
. Clearly,  is a critical point of
is a critical point of  if and only if
if and only if  is a solution of the equation
is a solution of the equation  and hence a solution of (3.2) and thus
and hence a solution of (3.2) and thus  is a solution of (3.1).
is a solution of (3.1).
Now, we suppose that there exists a real-bounded mapping  such that
such that

For  , let
, let

Since

equation (3.17) is equivalent to

Suppose that for  ,
,

and for  , define
, define

which is equivalent to

Since  is a self-adjoint operator, it possesses spectral resolution
is a self-adjoint operator, it possesses spectral resolution

with a right continuous spectral family  ; and we let
; and we let

for all  with
with  . Then, the operator
. Then, the operator  has the spectral resolution:
has the spectral resolution:

where  is an identity operator.
is an identity operator.
Define  and
and  by
by

By (3.21), we have

and hence

We need to prove a lemma before presenting our main theorem.
Lemma 3.1.
Suppose that  in (3.2) satisfies (3.20),
in (3.2) satisfies (3.20),  commutes with the linear operator
commutes with the linear operator  and satisfies (3.21),
and satisfies (3.21),  is a continuous function defined in (3.22). Then, for
is a continuous function defined in (3.22). Then, for 

Proof.
For  , let
, let

Note that  commutes with the linear operator
commutes with the linear operator  and
and

By (3.22),

Now, we show our main theorem dealing with (3.1).
Theorem 3.2.
Let  be a potential Carathéodory function satisfying (3.17). Suppose that
be a potential Carathéodory function satisfying (3.17). Suppose that  commutes with the linear operator
commutes with the linear operator  and satisfies
and satisfies

and the continuous function  defined by (3.23) satisfies the conditions
defined by (3.23) satisfies the conditions

Then, (3.1) has a unique solution  such that
such that

where  is a functional defined in (3.14) and
is a functional defined in (3.14) and  .
.
Proof.
For  , by Lemma 3.1, we have
, by Lemma 3.1, we have

Employing Theorem 2.1, we can know that there exists a unique  such that
such that  , where
, where  is a solution of (3.2) and this means that (3.1) has a unique solution
is a solution of (3.2) and this means that (3.1) has a unique solution  such that
such that

where  is a functional defined in (3.14) and
is a functional defined in (3.14) and  .
.
If the perturbation function  in (3.10) is a second Gâteaux differential, (3.17), (3.34), and (3.23) become
in (3.10) is a second Gâteaux differential, (3.17), (3.34), and (3.23) become



respectively. By (3.30) in Lemma 3.1, we have

where  .
.
We then have the following corollary of Theorem 3.2.
Corollary 3.3.
Let  be a potential Carathéodory function with first Gâteaux derivative
be a potential Carathéodory function with first Gâteaux derivative  satisfying (3.39) and (3.40) and
satisfying (3.39) and (3.40) and  commutes with the linear operator
commutes with the linear operator  . If the continuous function
. If the continuous function  defined by (3.41) satisfies (3.35), then (3.1) has a unique solution
defined by (3.41) satisfies (3.35), then (3.1) has a unique solution  and
and

where  is a functional defined in (3.14) and
is a functional defined in (3.14) and  .
.
References
Loud WS: Periodic solutions of nonlinear differential equations of Duffing type. In Proceedings of the U.S.-Japan Seminar on Differential and Functional Equations (Minneapolis, Minn., 1967). Benjamin, New York, NY, USA; 1967:199-224.
Ge W:
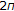 -periodic solutions of
-periodic solutions of  -dimensional Duffing type equation
-dimensional Duffing type equation  Chinese Annals of Mathematics A 1988,9(4):498-505. (Chinese)
Chinese Annals of Mathematics A 1988,9(4):498-505. (Chinese)Shen Z: On the periodic solution to the Newtonian equation of motion. Nonlinear Analysis: Theory, Methods & Applications 1989,13(2):145-149. 10.1016/0362-546X(89)90040-0
Li W:A necessary and sufficient condition on existence and uniqueness of
 -periodic solution of Duffing equation. Chinese Annals of Mathematics B 1990,11(3):342-345.
-periodic solution of Duffing equation. Chinese Annals of Mathematics B 1990,11(3):342-345.Ma R: Solvability of periodic boundary value problems for semilinear Duffing equations. Chinese Annals of Mathematics A 1993,14(4):393-399. (Chinese)
Mawhin J, Ward JR Jr.: Nonuniform nonresonance conditions at the two first eigenvalues for periodic solutions of forced Liénard and Duffing equations. The Rocky Mountain Journal of Mathematics 1982,12(4):643-654. 10.1216/RMJ-1982-12-4-643
Ding T, Zanolin F: Time-maps for the solvability of periodically perturbed nonlinear Duffing equations. Nonlinear Analysis: Theory, Methods & Applications 1991,17(7):635-653. 10.1016/0362-546X(91)90111-D
Manásevich RF: A nonvariational version of a max-min principle. Nonlinear Analysis: Theory, Methods & Applications 1983,7(6):565-570. 10.1016/0362-546X(83)90045-7
Li W, Shen Z: A globally convergent method for finding periodic solutions to the Duffing equation. Journal of Nanjing University 1997,33(3):328-336. (Chinese)
Huang W, Cao J, Shen Z:On the solution of nonlinear two-point boundary value problem
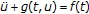 ,
, 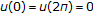 Applied Mathematics and Mechanics 1998,19(9):889-894. 10.1007/BF02458244
Applied Mathematics and Mechanics 1998,19(9):889-894. 10.1007/BF02458244Huang W, Shen Z: On the existence of solutions of boundary value problem of Duffing type systems. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics 2000,21(8):971-976. 10.1007/BF02428368
Manásevich RF: A min max theorem. Journal of Mathematical Analysis and Applications 1982,90(1):64-71. 10.1016/0022-247X(82)90044-0
Tersian SA: A minimax theorem and applications to nonresonace problems for semilinear equations. Nonlinear Analysis: Theory, Methods & Applications 1986,10(7):651-668. 10.1016/0362-546X(86)90125-2
Huang W, Shen Z: Two minimax theorems and the solutions of semilinear equations under the asymptotic non-uniformity conditions. Nonlinear Analysis: Theory, Methods & Applications 2005,63(8):1199-1214. 10.1016/j.na.2005.02.125
Huang W: Minimax theorems and applications to the existence and uniqueness of solutions of some differential equations. Journal of Mathematical Analysis and Applications 2006,322(2):629-644. 10.1016/j.jmaa.2005.09.046
Acknowledgment
The corresponding author is grateful to the referees for their helpful and valuable comments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 2.0 International License (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/2.0), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
About this article
Cite this article
Ting, Z., Wenhua, H. The Existence and Uniqueness of Solution of Duffing Equations with Non-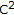 Perturbation Functional at Nonresonance.
Bound Value Probl 2008, 859461 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1155/2008/859461
Perturbation Functional at Nonresonance.
Bound Value Probl 2008, 859461 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1155/2008/859461
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1155/2008/859461
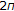 -periodic solutions of
-periodic solutions of  -dimensional Duffing type equation
-dimensional Duffing type equation  Chinese Annals of Mathematics A 1988,9(4):498-505. (Chinese)
Chinese Annals of Mathematics A 1988,9(4):498-505. (Chinese) -periodic solution of Duffing equation. Chinese Annals of Mathematics B 1990,11(3):342-345.
-periodic solution of Duffing equation. Chinese Annals of Mathematics B 1990,11(3):342-345.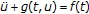 ,
, 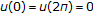 Applied Mathematics and Mechanics 1998,19(9):889-894. 10.1007/BF02458244
Applied Mathematics and Mechanics 1998,19(9):889-894. 10.1007/BF02458244